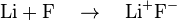Ionic bond
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
An ionic bond (or electrovalent bond) is a type of chemical bond based on electrostatic forces between two oppositely-charged ions. In ionic bond formation, a metal donates an electron, due to a low electronegativity to form a positive ion or cation. In ordinary table salt (NaCl), the bonds between the sodium and chloride ions are ionic bonds. Often ionic bonds form between metals and non-metals. The non-metal atom has an electron configuration just short of a noble gas structure. They have high electronegativity, and so readily gain electrons to form negative ions or anions. The two or more ions are then attracted to each other by electrostatic forces.
Ionic bonding occurs only if the overall energy change for the reaction is favourable – when the bonded atoms have a lower energy than the free ones. The larger the resulting energy change the stronger the bond.
Pure ionic bonding is not known to exist. All ionic bonds have a degree of covalent bonding or metallic bonding. The larger the difference in electronegativity between two atoms the more ionic the bond. Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or in solution. They generally have a high melting point and tend to be soluble in water.
Contents
|
[edit] Polarization effects
Ions in crystal lattices of purely ionic compounds are spherical; however, if the positive ion is small and/or highly charged, it will distort the electron cloud of the negative ion. This polarization of the negative ion leads to a build-up of extra charge density between the two nuclei, i.e., to partial covalency. Larger negative ions are more easily polarized, but the effect is usually only important when positive ions with charges of 3+ (e.g., Al3+) are involved (e.g., pure AlCl3 is a covalent molecule). However, 2+ ions (Be2+) or even 1+ (Li+) show some polarizing power because their sizes are so small (e.g., LiI is ionic but has some covalent bonding present).
[edit] Ionic structure
Ionic compounds in the solid state form a continuous ionic lattice structure in an ionic crystal. The simplest form of ionic crystal is a simple cubic. This is as if all the atoms were placed at the corners of a cube. This unit cell has a wht that is the same as 1 of the atoms involved. When all the ions are approximately the same size, they can form a different structure called a face-centered cubic (where the weight is 4 * atomic weight), but, when the ions are different sizes, the structure is often body-centered cubic (2 times the weight). In ionic lattices the coordination number refers to the number of connected ions.
[edit] Ionic versus covalent bonds
In an ionic bond, the atoms are bound by attraction of opposite ions, whereas, in a covalent bond, atoms are bound by sharing electrons. In covalent bonding, the molecular geometry around each atom is determined by VSEPR rules, whereas, in ionic materials, the geometry follows maximum packing rules.
[edit] Electrical conductivity
Ionic substances in solution conduct electricity because the ions are free to move and carry the electrical charge from the anode to the cathode. Ionic substances conduct electricity when molten because atoms (and thus the electrons) are mobilised. Electrons can flow directly through the ionic substance in a molten state.
[edit] Substances in ionic form
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||