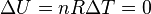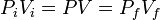Isothermal process
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
An isothermal process is a thermodynamic process in which the temperature of the system stays constant: ΔT = 0. This typically occurs when a system is in contact with an outside thermal reservoir (heat bath), and processes occur slowly enough to allow the system to continually adjust to the temperature of the reservoir through heat exchange. An alternative special case in which a system exchanges no heat with its surroundings (Q = 0) is called an adiabatic process.
Consider an ideal gas, in which the temperature depends only on the internal energy, which is a function of the mean translational kinetic energy of the molecules, as given by a Boltzmann distribution; if the internal energy is constant, so is the temperature. Take the number of moles n as a constant.
but this means, according to the ideal gas law, that
so that
where Pi and Vi are the pressure and volume of the initial state, Pf and Vf are the pressure and volume of the final state, and the variables P and V stand for the pressure and volume of any intermediate state during an isothermal process.
Curves called isotherms appear as a hyperbolas on a P-V (pressure-volume) diagram (T = constant). Each one asymptotically approaches both the V (abscissa) and P (ordinate) axes. This corresponds to a one-parameter family of curves, a function of T, whose equation is
By the first law of thermodynamics, the isotherms of an ideal gas are also determined by the condition that
where W is work done on the system. (While Q and W are incremental quantities, they do not represent differentials of state functions.) This means that, during an isothermal process, all heat accepted by the system from its surroundings must have its energy entirely converted to work which it performs on the surroundings. That is, all the energy which comes into the system comes back out; the internal energy and thus the temperature of the system remain constant.
In a minute process of this process, the minute work dW can be shown as follow.
- dW = Fdx = PSdx = PdV
Therefore the entire work of the process from A to B is shown with the integration of the previous equation.
Here, by the ideal gas equation,
Therefore in the isothermal process, the following equation is formed.
Isothermal processes can occur in any kind of system, including highly structured machines, and even living cells. Various parts of the cycle of some heat engines are carried out isothermally and may be approximated by a Carnot cycle.