Weak acid
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Acid-base extraction
- Acid-base reaction
- Acid dissociation constant
- Acidity function
- Buffer solutions
- pH
- Proton affinity
- Self-ionization of water
- Acids:
- Lewis acids
- Mineral acids
- Organic acids
- Strong acids
- Superacids
- Weak acids
- Bases:
- Lewis bases
- Organic bases
- Strong bases
- Superbases
- Non-nucleophilic bases
- Weak bases
edit
A weak acid is an acid that does not ionize in solution to a significant extent; that is, if the acid was represented by the general formula HA, then in aqueous solution a significant amount of undissociated HA still remains. Weak acids in water dissociate as
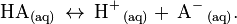
The equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products are related by the Acidity constant expression, (Ka):
![\mathrm{ K_a\, =\, \frac {[H^+\,][A^-\,]}{[HA]} }](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/e/1/1/e1160cb29e6e647fa04612aee2af4f35.png)
The greater the value of Ka, the more the formation of H+ is favored, and the lower the pH of the solution. The Ka of weak acids varies between 1.8×10-16 and 55.5. Acids with a Ka less than 1.8×10-16 are weaker acids than water. Acids with a Ka of greater than 55.5 are strong acids and almost totally dissociate when dissolved in water. The vast majority of acids are weak acids. Organic acids are a large subset of weak acids. Common household weak organic acids include acetic acid found in vinegar, and citric acid found in lemons; weak mineral acids include boric acid used as an antiseptic and eyewash and phosphoric acid that appears in many soft drinks.
